
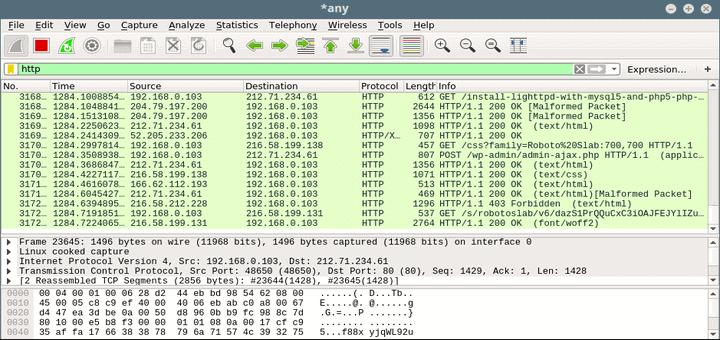
 Users can watch traffic over the network.
Users can watch traffic over the network. 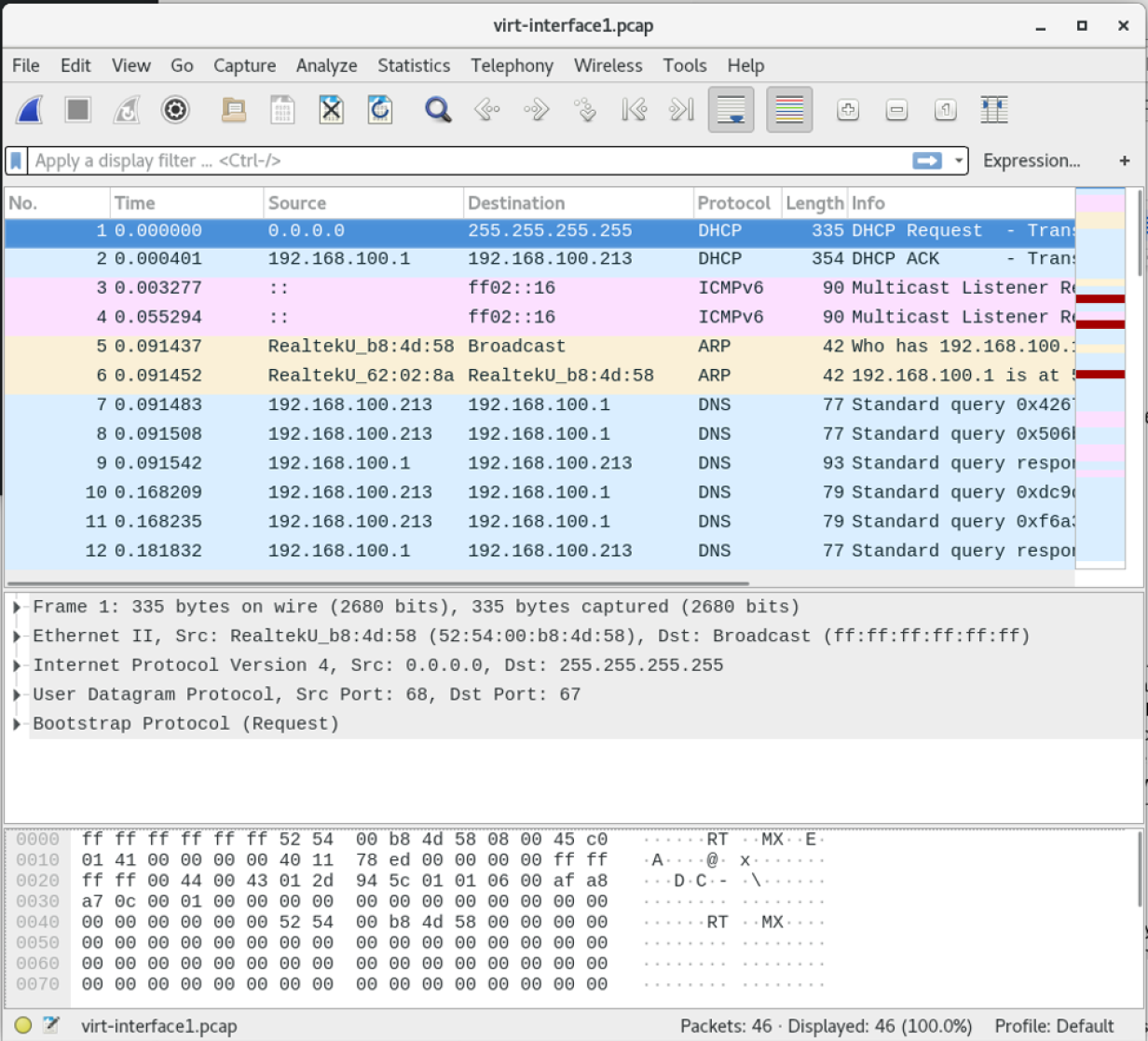 Network security engineers use it to examine security problems. These packets are of small size and can be viewed in Wireshark. What is packet?Ī packet is a unit of data that is transmitted over a network between the source and destination hosts. Otherwise, it'll only happen when the network is explicitly configured to let it happen.Wireshark is an open-source packet analyzer that can be used to capture, filter, and inspect the network. Simply installing Wireshark is not enough, some other action needs to be taken. But it is possible.ĪRP Spoofing is the only way for a computer with no special network privileges to sniff another network node's traffic, and that depends on whether or not the network switch defends against that kind of action. Again, the names vary, and the network topology has to be just right. Different Subnet entirely If Computer B is on a different subnet entirely, the only way this works is if the router core support a remote monitoring solution. Same Subnet, evil method If the router isn't terribly secure either, the ARP Spoofing attack will work for an entire subnet!.
Network security engineers use it to examine security problems. These packets are of small size and can be viewed in Wireshark. What is packet?Ī packet is a unit of data that is transmitted over a network between the source and destination hosts. Otherwise, it'll only happen when the network is explicitly configured to let it happen.Wireshark is an open-source packet analyzer that can be used to capture, filter, and inspect the network. Simply installing Wireshark is not enough, some other action needs to be taken. But it is possible.ĪRP Spoofing is the only way for a computer with no special network privileges to sniff another network node's traffic, and that depends on whether or not the network switch defends against that kind of action. Again, the names vary, and the network topology has to be just right. Different Subnet entirely If Computer B is on a different subnet entirely, the only way this works is if the router core support a remote monitoring solution. Same Subnet, evil method If the router isn't terribly secure either, the ARP Spoofing attack will work for an entire subnet!. 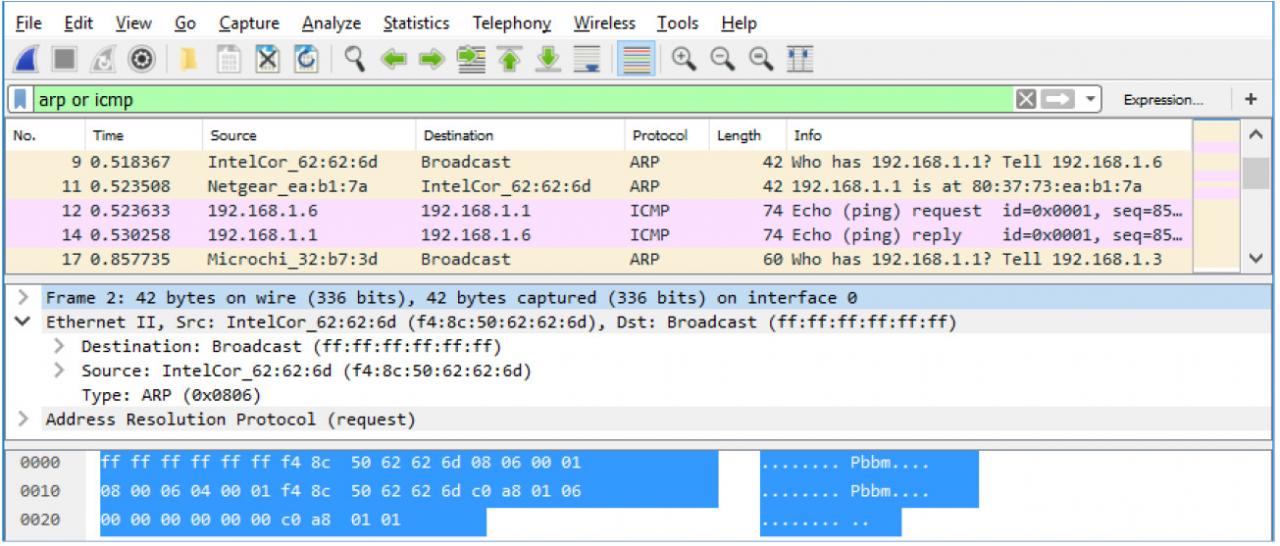
This doesn't work on all switches, and some network stacks reject this kind of thing. For this to work, Computer B then has to send it off to the real gateway. Clients that accept the ARP packet rewrite their IP:MAC-Address lookup table with the bad address in it, and proceed to send all off-subnet traffic to Computer B. Computer A issues an ARP packet telling the subnet that it is actually the gateway address, even though it isn't.
Same Switch, evil method If both computers are on the same network switch, and the switch is not terribly secure, it is possible to perform what's known as a ARP Spoofing attack. That will allow Wireshark on Computer A to see the traffic. Same Switch, good method If both computers are on the same network switch, and the switch is managed, it is probably possible to configure it to span/mirror/monitor (the terms change with vendor) traffic for Computer B's port onto Computer A's port. There are several ways of getting it there. if your network supports it, the network itself can show Computer A the traffic for Computer B, and from there Wireshark can grab it. In general, no, Wireshark can't sense that traffic.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
